Nucleotides / Lipids
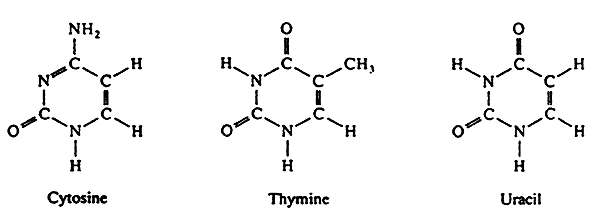
Pyrimidines

Purines
| Base | Ribonucleoside |
Ribonucleotide |
| (Base + Ribose) | (Base + Ribose + Phos.) | |
| Adenine(A) | Adenosine | Adenosine 5'-monophosphate(AMP) |
| Guanine(G) | Guanosine | Guanosine 5'-monophosphate(GMP) |
| Cytosine(C) | Cytidine | Cytidine 5'-monophosphate(CMP) |
| Uracil(U) | Uridine |
Uridine 5'-monophosphate(UMP) |
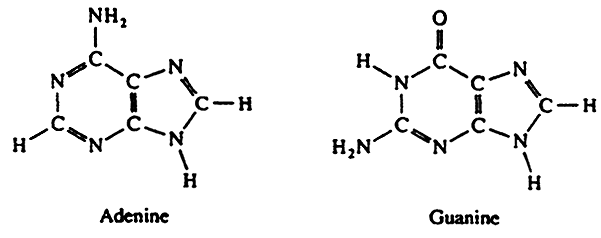
Ribose:
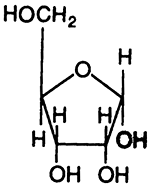
A "Ribonucleoside", A "Deoxyribonucleoside", A "Ribonucletide"
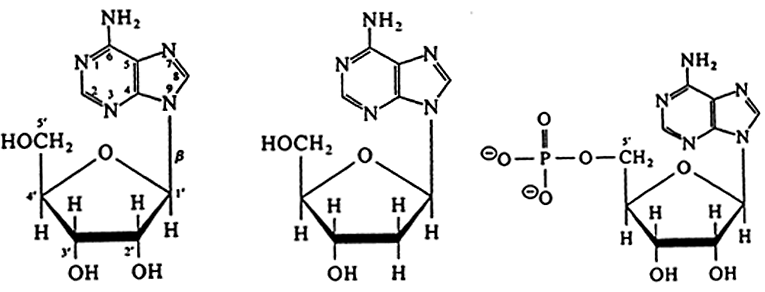
AMP
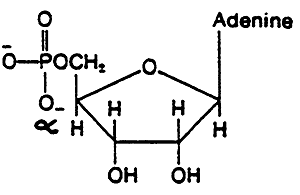
ADP
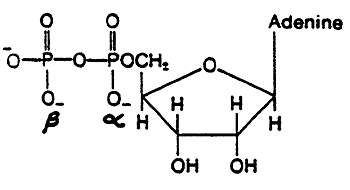
ATP
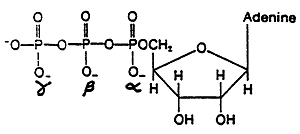
Ribonucleotides are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides (ribonucleotides) can be linked sequentially to form nucleic acids (store and transmit genetic information).
Nucleotide Derivatives:
Many biosynthetic reactions in carbohydrate metabolism require nucleotide derivatives.
i.e. Glucose-1-phosphate + ATP ----> ADP-glucose
Lipids:
Large group of biomolecules soluble only in hydrophobic (non-polar) solvents.
Can be subdivided into:
fatty acids.
phospholipids.
steroids.
Fatty Acids:
-have an acidic head group and a long hydrocarbon tail.
-saturated (no -C=C-), unsaturated (-C=C-), polyunsaturated
Some Common Fatty Acids:
Myristic CH3(CH2)12COOH
Palmitic CH3(CH2)14COOH
Oleic CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH
Linoleic CH3(CH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CH2)7COOH
Linolenic CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CH2)7COOH
Arachidonic CH3(CH2)3(CH2CH=CH)4(CH2)3COOH
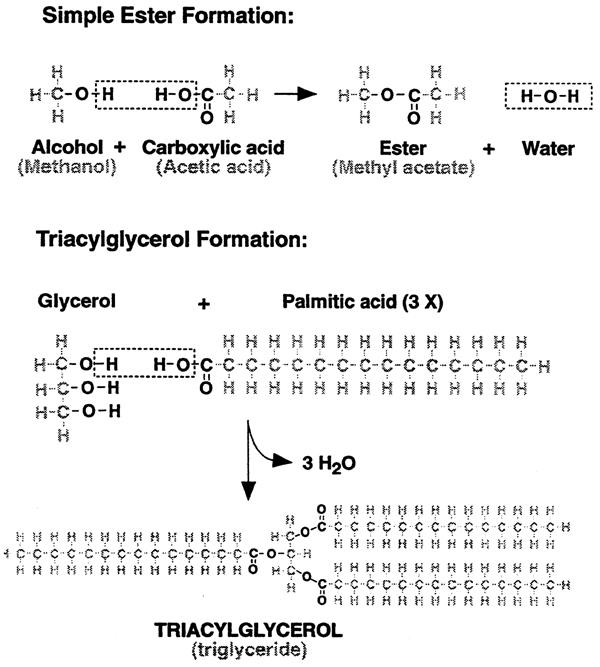
Triacylglycerol Formation: storage form of fatty acids
Glycerol + Palmitic Acid (x3)
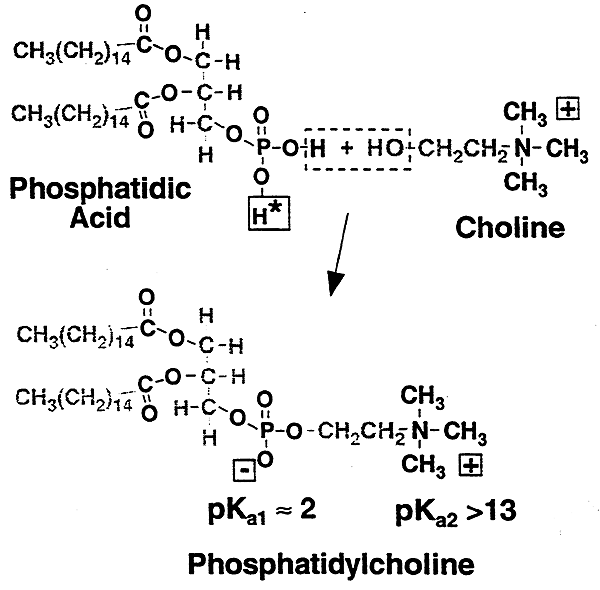
Phospholipids:
Most prevalent class of lipids in membranes.
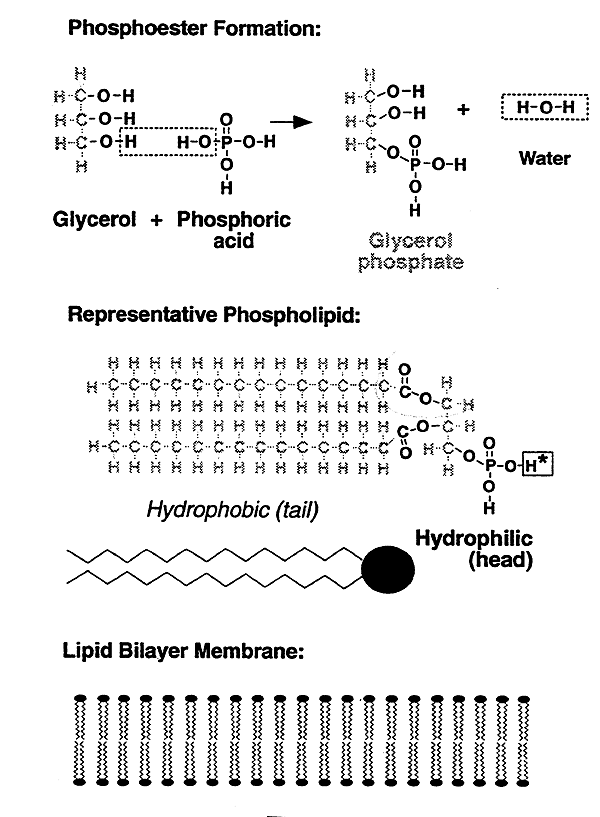
Variations.......
Phospholids can have one of their oxygens on the phosphate group attached to:
Choline -O-CH2CH2N(CH3)3
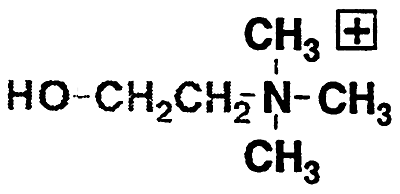
Ethanolamine -O-CH2CH2NH3
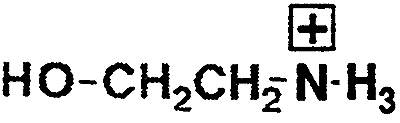
Serine -O-CH2CH(+NH3)(CO2-)
Inositol
Dipalmitoyl Phosphatidylcholine (DPPC), "Lecithin"
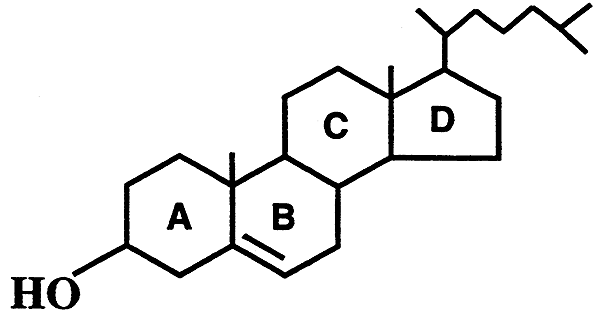
Steroids:
Cholesterol
Clinical Correlate: Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome
-In utero, the developing fetus exists in a fluid environment, the lungs are collapsed (oxygenation occurs across the placenta).
-At birth the newborn is suddenly exposed to air, the lungs must expand and fill w/ air.
-Because of the high surface tension, caused by H-bonding of water molecules, this requires a significant amount of energy.
-The energy barrier is decreased with Lung Surfactant: phospholipids, primarily DPPC (Lecithin) and proteins. These amphiphilic compounds form "sheets" in an aqueous environment reducing the surface tension between water molecules and decreasing the energy barrier.
-This surfactant prevents lung collapse in newborns as well as adults.
-Premature infants are deficient in surfactant.
-Hyaline Membrane Disease is defined as progressive respiratory failure in premature infants caused by inadequate surfactant and structurally immature lungs.
-Survanta is an artificial surfactant comprised of bovine lung extract containing phospholipids and proteins, with added lecithin.
-When administered to premature infants it mimics the surface tension lowering properties of natural lung surfactant -----> allowing CO2to escape the lungs and oxygenation of the blood.
© Dr. Noel Sturm 2020