Citric Acid Cycle
Acetyl CoA Metabolism
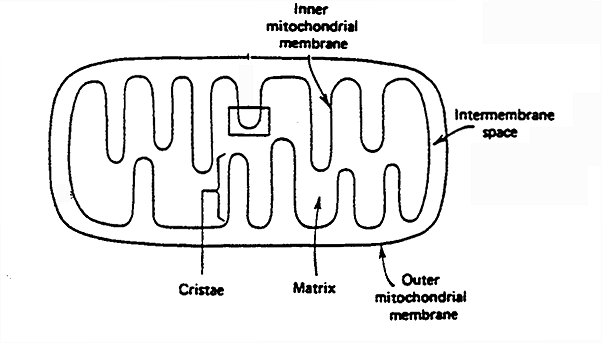
Mitochondria: Structure and Function

1. Outer Mitochondrial Membrane:
(a) a barrier to molecules w/ MW greater than 10,000
2. Intermembrane Space
(a) houses enzymes specific to mitochondria
3. Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
(a) allows diffusion only of small (<100 MW) uncharged molecules
(b) allows for very specific control of the flow of biomolecules into and out of mitochondrian
(c) Cristae- indentations that increase the surface area of the membrane
(d) contains: the components of electron transport, enzymes for the citric acid cycle
4. Matrix
Contains enzymes for:
(a) pyruvate decarboxylation
(b) citric acid cycle
(c) fatty acid b-oxidation
(d) ketone body synthesis (liver)
(e) ketone oxidation (other tissues)
(f) some amino acid metabolism
(g) some gluconeogenesis
Cytosol: Glycolysis and most of Gluconeogenesis
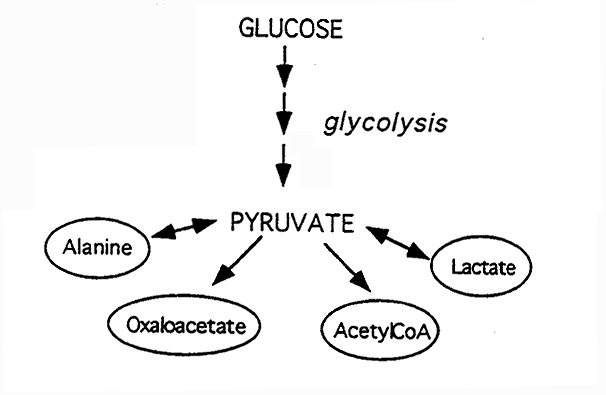
Metabolic Fates of Pyruvate:
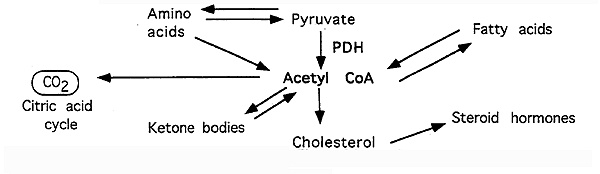
Metabolism of Acetyl CoA:
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDH): a multi-enzyme complex
Pyruvate + CoA + NAD+------------> CO2 + Acetyl CoA + NADH + H+
Thiamine diphosphate (TDP):
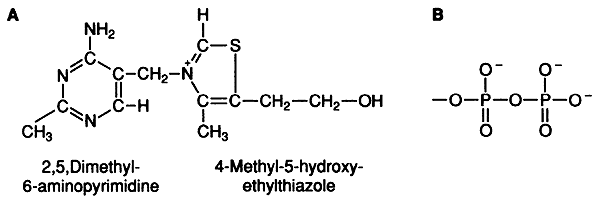
Lipoate:
Coenzyme A:
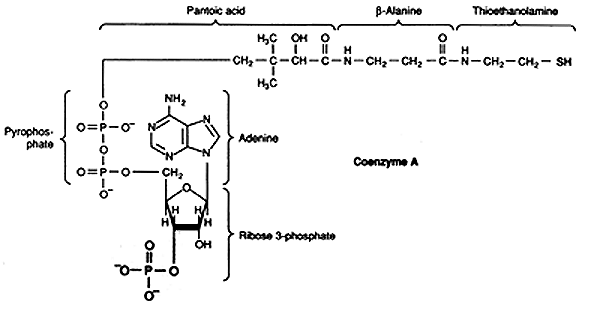
Acetyl CoA:
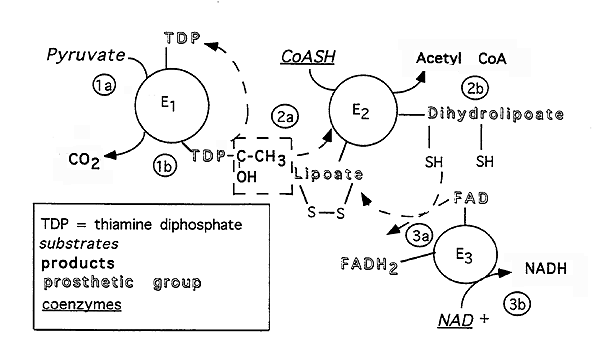
STEP 1a: Pyruvate binds to E1.
STEP 1b: Pyruvate reacts with TDP causing the release of CO2 and formation of TDP- CH(OH)CH3
STEP 2a: Lipoate is acetylated by TDP-CH(OH)CH3 with oxidation of the alcohol to a keto group and reduction of the lipoate disulfide bond. TDP is regenerated.
STEP 2b: Acetylated lipoate reacts with Coenzyme A (CoASH) to form acetyl CoA and reduce lipoate to dihydrolipoate.
STEP 3a: Reduced lipoate is oxidized by FAD, with the production of FADH2.
STEP 3b: FAD is regenerated by the oxidation of FADH2 by NAD+, yielding NADH.
Regulation:
Feedback Inhibition: - Acetyl CoA and NADH
What goes IN: Pyruvate, CoASH, NAD+
What comes OUT: Acetyl CoA, NADH, CO2
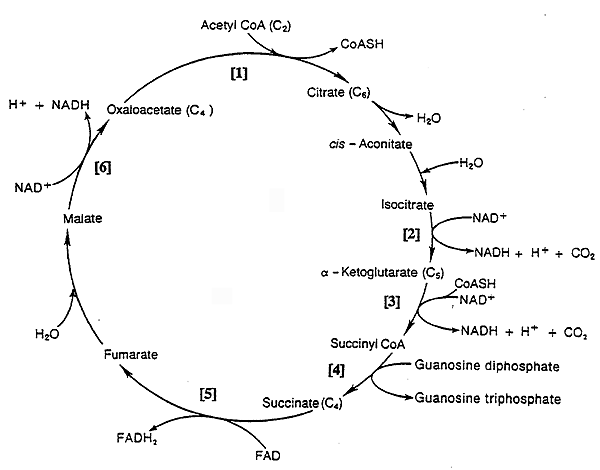
Citric Acid Cycle / Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA Cycle):
[1] Citrate Synthase: exergonic, spontaneous; condenses acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate. The CoA produced is used to produce acetyl CoA via PDH.
[2] Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: oxidation-reduction reaction, first site for NADH production.
[3] a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase: oxidation-reduction reaction, second NADH is produced. Feedback inhibited by succinyl CoA.
[4] Succinyl CoA Synthetase: substrate level phosphorylation. GTP + ADP <---> GDP + ATP
[5] Succinate Dehydrogenase: oxidation-reduction reaction, FADH2 is produced.
[6] Malate Dehydrogenase: oxidation-reduction reaction, third NADH is produced.
Energy Production:
1 NADH = 3 ATP
1 GTP = 1 ATP
1 FADH2 = 2 ATP
3 ATP Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (from NADH)
3 ATP Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (from NADH)
3 ATP a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (from NADH)
1 ATP Succinyl CoA Synthetase (from GTP)
2 ATP Succinic Dehydrogenase (from FADH2)
3 ATP Malate Dehydrogenase (from NADH)
Total: 15 ATP (12 ATP / Turn of TCA Cycle)
Remember we get 2 Acetyl CoA molecules for each Glucose molecule so the Grand Total is: 30 ATP!
Regulation:
|
Enzyme
|
Inhibition
|
Stimulation
|
|
Citrate
Synthase
|
Succinyl
CoA, ATP
|
|
|
Isocitrate
DH
|
NADH, ATP
|
ADP
|
|
a-KG
DH
|
Succinyl
CoA, NADH, GTP
|
© Dr. Noel Sturm 2020